| A | B |
|---|
| TRUE or FALSE: It requires higher temperatures to fuse bigger nuclei like carbon or silicon than it does to fuse smaller nuclei like hydrogen. | TRUE |
Which letter on the diagram represents where a star would be if it was in the stable main stage of it's lifecycle where it spends most of it's time?,  | C, 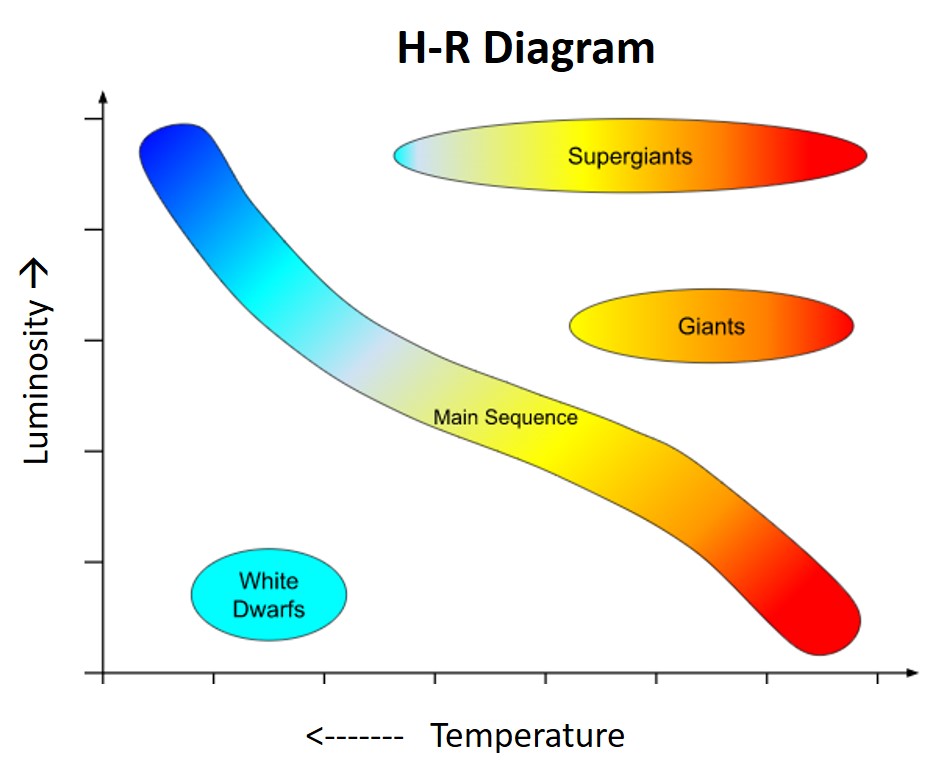 |
Which letter on the diagram represents where a star would be if it was using hydrogen as its main source of fuel?,  | C (All stars on the main sequence are still using hydrogen as their fuel for fusion. It isn't until a star runs out of hydrogen that it leaves the main sequence and starts fusing heavier elements starting with helium),  |
Which letter on the diagram represents where a star would be if it was on the "Main Sequence"?,  | C,  |
Which letter or letters on the diagram represents a possible location for a star that is near the end of it's life?,  | A,B,and D,  |
Which number on the diagram would our Sun be closest to?,  | 4 (That's right. Our Sun is currently a main sequence yellow star),  |
Which number on the diagram would our Sun be closest to just before it starts to become unstable and starts to die?,  | 3 (That's right. As stars age on the main sequence, they get hotter and more luminous, moving up and to the left)),  |
Which letter on the diagram would our Sun be closest to when it first leaves the main sequence during the final parts of it's life?,  | B (That's right. After our Sun has stopped fusing hydrogen, it will leave the main sequence, start fusing helium, and greatly increase in science to become a Giant for a short period of time.,  |
What is the next labeled step in the stellar evolution of Giants?,  | White Dwarfs (They lose much of their mass by blowing it out toward space, then contract and shrink into hot white dwarfs),  |
Near which letter in the diagram below would you find Supergiants?,  | A,  |
Near which number in the diagram below would you find Red Dwarfs?,  | 5,  |
Near which letter or number would you find stars who will become, or just were, black dwarfs?,  | D (Yes, White Dwarfs will slowly cool down and fade into black dwarfs),  |
Near which number would you find the oldest stars in the universe?,  | 5 (That's right, red dwarfs burn so slowly that they can last a trillion years. The larger and hotter a star, the faster it uses up it's fuel),  |
Near which number would you find low mass stars?,  | 5,  |
Near which number or numbers would you find stars that never become Giants or Red Giants, but instead go straight to the White Dwarf Stage after they leave the main sequence?,  | 5 (That's right. Only the lowest mass stars, the Red Dwarfs, turn straight into White Dwarfs without ever going through a Giant or Supergiant phase first),  |
Next to which LETTER would you find stars that end their lives in one huge explosion?,  | A (Yes, it's the SuperGiants and Hypergiants (not labeled on this diagram) that end their lives in one big Supernova explosion),  |
Next to which number would you find a star that is most likely to have its core end up as a black hole?,  | 1 (Yes, these massive blue giant stars on the main sequence will end up as the biggest stars of all, hypergiants, which will go Supernova leaving behind and impossibly dense core with gravity so great that not even light can escape from it). |
| What can escape from a black hole? | Chuck Norris, but other than that, nothing, not even light.,  |
Next to which number would you find a star that is most likely to have its core end up as a neutron star?,  | 2 (Yes, these blue giants will become Super Red Giants, explode as a Supernova, and leave the core to collapse the electrons into the protons, turning them into neutrons, due to the intense gravity. Only the very biggest Blue Giants near the number 1 will become the Hypergiants that will end up as a black hole after they explode),  |
Which letter is next to the type of stars that can explode over and over again as Novas if they are involved with a white dwarf as a binary star system?,  | B (Yes Giants involved with white dwarfs in a binary star system can go Nova, but it's actually the white dwarf that does the exploding because it's compact size and high density gives it high surface gravity which can suck outer atmosphere gases off the Red Giant, causing the white dwarf to destabilize and explode, but not get destroyed) |
Which letter is next to the type of stars that can explode over and over again as Novas if they are involved with a Red Giant as a binary star system?,  | D (Yes, white dwarfs can go nova by pulling gases away from Red Giants because it's compact size and high density gives it high surface gravity which can suck outer atmosphere gases off the Red Giant, causing the white dwarf to destabilize and explode, but not get destroyed),  |
Next to which letter or number would you find the most massive stars?,  | 1 (Don't confuse mass with size. The hottest stars on the main sequence are the most massive, which also means they have the most gravity and therefore pressure, so they burn through their fuel the fastest achieving super high temperatures and luminosities. When they leave the main sequence, they expand into much bigger Red Giants and Hypergiants, but these stars are blowing gases from their outer layers off into space, so they are losing mass at the same time they are growing in size, so they aren't as massive), 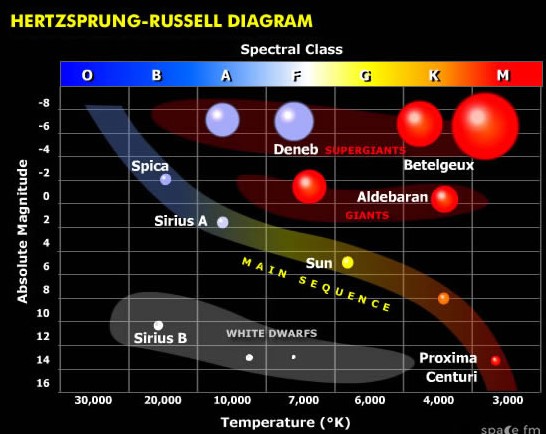 |
Next to which letter or number would you find the biggest stars?,  | A (Yes, the Supergiants (and Hypergiants not pictured) and the biggest stars in the Universe. The biggest star we know of it about 2000 times the diameter of the Sun and would swallow Saturn if it were our star),  |
Next to which number would you find the stars that spend the shortest amount of time on the main sequence?,  | 1 (Yes, these stars are the hottest. Even though they are also the most massive stars on the main sequence with the most fuel, they burn through it very quickly due to the high temperatures and pressures within the core of the star) |
TRUE or FALSE: Stars stay in one place on H-R diagrams throughout the time they spend on the main sequence.,  | FALSE (Stars get hotter and more luminous as they use up their hydrogen and their cores get denser, so they move up and to the left as they age on the main sequence.),  |
| Low mass main sequence stars are also called _______ and have masses of ________ that of the sun. | Red dwarfs, a third or less |
| What is the relationship between the mass of a main sequence star and its lifespan? | The higher the mass, the shorter its lifespan (this is because higher mass stars have more pressure due to gravity and therefore burn hotter so they can fuse their fuel and run out of it a lot faster) |
| _____ mass stars will only fuse hydrogen during their lifetime, unlike all other stars that will switch over to helium and some to even heavier elements during their lifetime. | Low |
| Right after low mass stars leave the main sequence, they become ______. | white dwarfs |
| Medium mass stars have a mass from ____ the mass of the Sun up to ____ the mass of the Sun. | 1/3rd, 8 times |
| Medium mass stars become ________ after leaving the main sequence, then shrink down into _______ and eventually dim into _________. | Red Giants, white dwarfs, black dwarfs |
| Our Sun is a _______ mass star. | medium |
| Medium mass stars start out fusing ______ , then later on they fuse _______ leading to a build-up of _______ in their core (which they can't fuse into bigger elements) | hydrogen, helium, carbon |
________ Nebulae (pictured here) are clouds of gas that came from a Red Giant and are now being illuminated by the white dwarf that remains of the star.,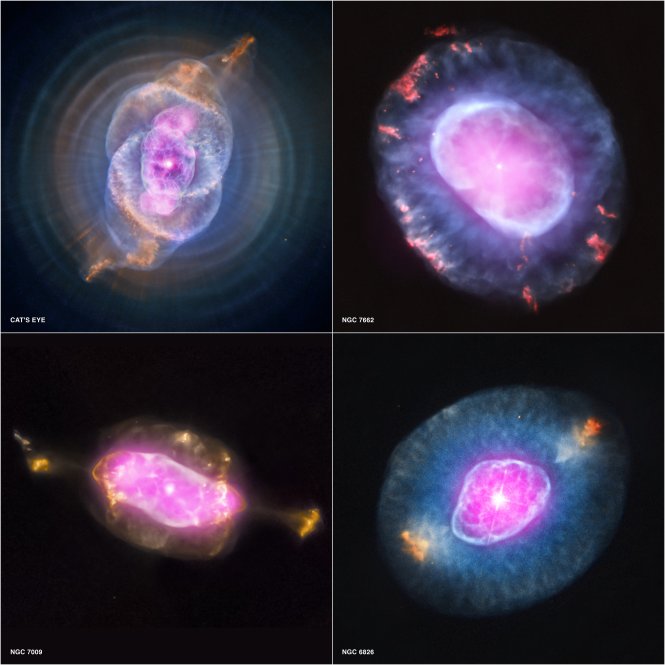  | Planetary,  |
What is illuminating these balls of gas called Planetary Nebulae?,  | A white dwarf at the center (The white dwarf is all that remains of the Red Giant that blew off its outer layers of gas long ago),  |
| The biggest stars in the Universe are called __________ while the second biggest stars in the Universe are called ______. | Hypergiants, Supergiants (These stars can be up to 2000 times the diameter of the Sun), 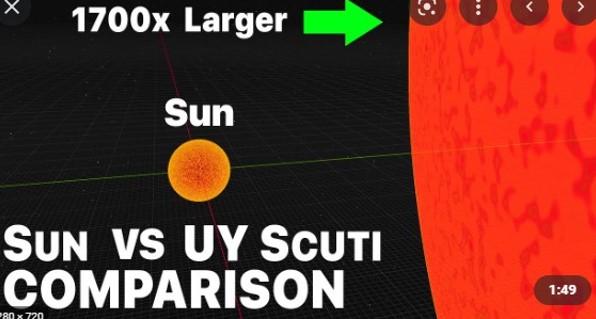 |
| The heaviest element that can be made inside a star (before it explodes) is _____. | iron |
| When Supergiants and Hypergiants explode, the explosion is called a(n) ______. | Supernova |
| What has to happen in order to make any element larger than iron? | A star has to explode in a Supernova. |
| When a Supernova occurs, the left-over core usually collapses into a small dense mass called a(n) ______ and if the star is really really big, the core could totally collapse and become a(n) ______ | neutron star, black hole |
| The gravitational force near the surface of a black hole is so great that nothing, not even ____, can escape. | light |
| A star that is made up of two stars orbiting each other is called a(n) ______. | binary star (A third to a half of all stars in the Universe are multiple star systems made up of 2 or more stars orbiting each other, including the North Star (Polaris) and Sirius (the brightest star in the night sky),  |
| A white dwarf orbiting a Red Giant can end up exploding over and over again in an event called a(n) ______ due to pulling gasses away from the Red Giant and becoming temporarily unstable. | Nova,  |
| The further apart two stars are in a binary star system, the ______ they orbit each other. | slower (Notice how these binary stars change their speed as they get closer and further from each other), 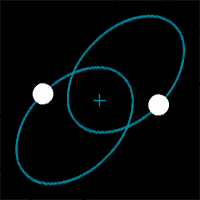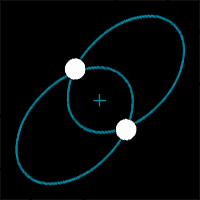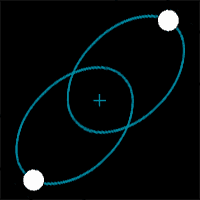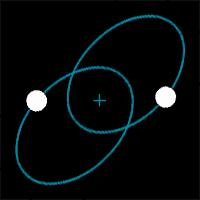 |
| A(n) _____ is a large-scale group of stars, gas, and dust that is bound together by gravity. | galaxy |
| Most galaxies are thought to have a supermassive _____ at the center. | black hole |
Which type of galaxy is pictured here?,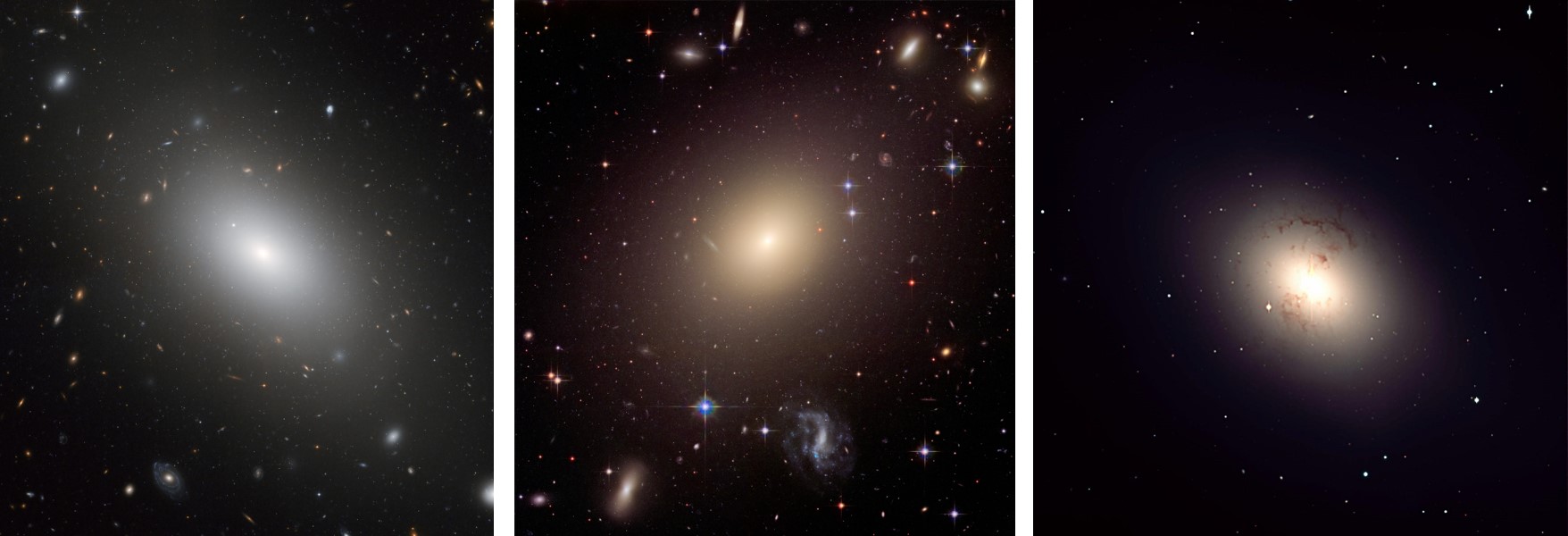  | Elliptical,  |
| Which type of galaxy has mostly small old stars and little gas or dust? | Elliptical |
Which type of galaxy is pictured here?,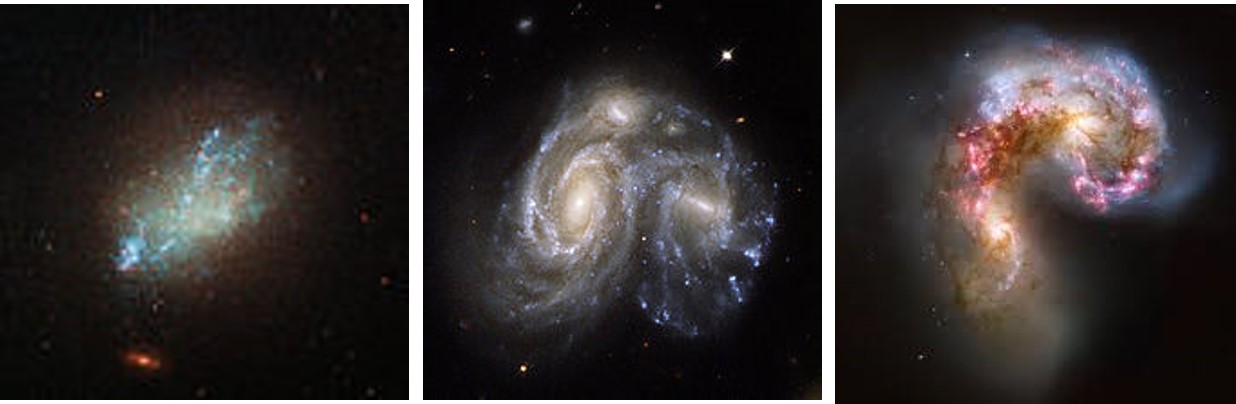  | Irregular,  |
| Which type of galaxies have no defined shape and may include galaxies that are merging? | Irregular,  |
| Which type of galaxies have a flattened disc shape and arms? | Spiral,  |
Which type of galaxy is pictured below?,  | Spiral,  |
| Which type of galaxy is our Milky Way classified as? | Spiral,  |
In which region of this galaxy would you find large bright young stars? (You can name it or give the letter), 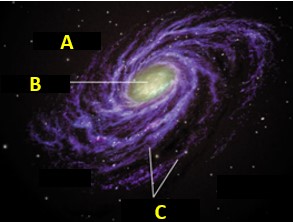 | Spiral arms (C),  |
The area labeled C is called ____.,  | the spiral arms,  |
The area labeled B is called ____.,  | the bulge |
The area labeled A is called ____.,  | the halo (the halo is an elliptical shaped region surrounding the arms of the spiral galaxy. It's basically the outer region)),  |
What type of stars are found in the halo of the Milky Way?,  | small old stars (The gases in this region of the Milky Way were used up long ago to create a massive number of stars. Only the smallest longest living stars are still there),  |
Which type of galaxies send an extremely strong beam of light and matter from the black hole area out in both directions perpendicular to the flattened disc portion of the galaxy?, .jpg) | Active Galaxies (Quasars are a type of active galaxy), .jpg) |