| A | B |
|---|
| meth in the name | 1 C |
| eth in the name | 2C |
| prop in the name | 3C |
| but in the name | 4C |
| pent in the name | 5C |
| hydrocarbon | contains C & H only |
| saturated | contains single bonds only |
| unsaturated | contains a C=C double bond |
| Homologous series of unsaturated hydrocarbons | alkenes |
| Homologous series of saturated hydrocarbons | alkanes |
| isomerism | 2 or more compounds same molecular formula different structures |
| Alkanes general formula is | CnH2n+2 |
| Alkenes general formula is | CnH2n |
| C2H4 is an... | alkene |
| CH4 is an ... | alkane |
| CH4 name | methane |
| C2H4 name is | ethene |
| C3H6 name is | propene |
| C4H8 name is | butene |
| C4H10 name is | butane |
The compounds here are examples of, 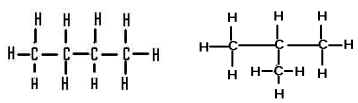 | isomers (structural) |
The compounds here are examples of, 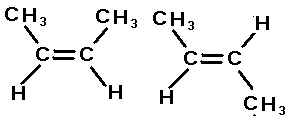 | geometric isomers |
| The structural formula of methane is | 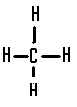 |
| The structural formula of ethene is | 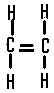 |
| The structural formula of propene is | 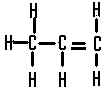 |
| The structural formula of butane is | 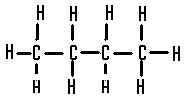 |
| An isomer of butane is | 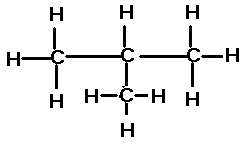 |
The name of this compound is,  | 2-methyl propane |
This is a ........ alcohol, 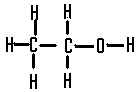 | primary |
This is a ......... alcohol, 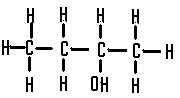 | secondary |
This is a ......... alcohol, 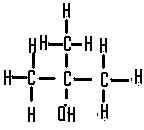 | tertiary |
| the structural formula of ethanol is | 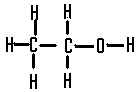 |
| An isomer of ethanol is | CH3OCH3 |
This isthe functional group present in, 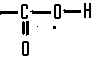 | a carboxylic acid |
This is called, 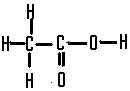 | ethanoic acid |
This belongs to an homologous series called, 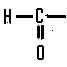 | aldehydes |
| In structural formulae carbon always has ...... bonds | 4 |
| In structural formulae hydrogen always has ...... bonds | 1 |
| In structural formulae oxygen always has ...... bonds | 2 |
This compound is called, 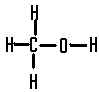 | methanol |