| A | B |
|---|
Fault, 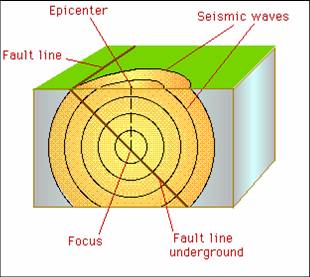 | A break or crack in the earth's crust along where there is movement |
Where do most earthquakes occur?, 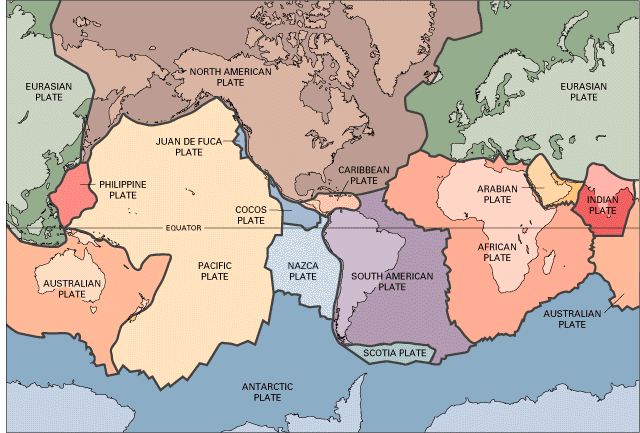 | near plate boundaries |
| An earthquake measuring 2.9 on the Richter Scale would be | Mild |
| Cause of earthquakes | slippage along faults in Earth's crust |
| Folding | A bend in a layer of rock |
Anticline, 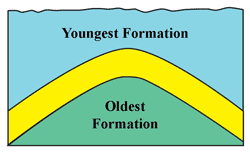 | An upward fold - hill - ie. Appalachian Mts. |
Syncline, 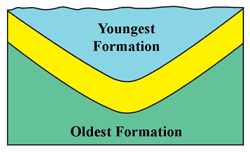 | Downward fold - a valley |
| What type of fault is the San Andreas Fault | Lateral/Transform/Strike Slip |
| What does the Richter Scale determine? | The strength of the earthquake |
| The higher the number on the Richter Scale means... | the stronger the earthquake |
| How many seismic stations are needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake | Three |
Triangulation, 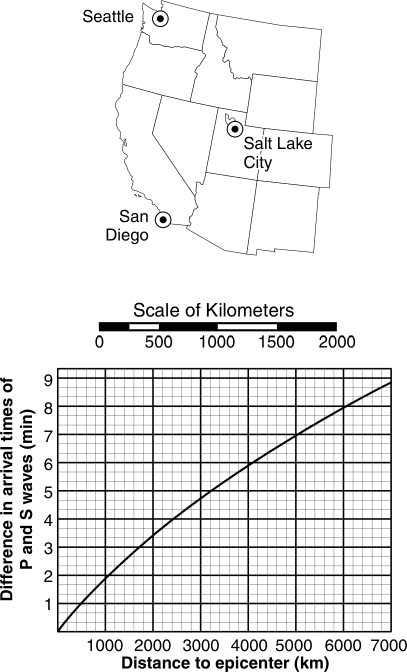 | The method of locating an earthquake's epicenter |
| A rock that fractures and then moves is called a... | Fault |
Focus, 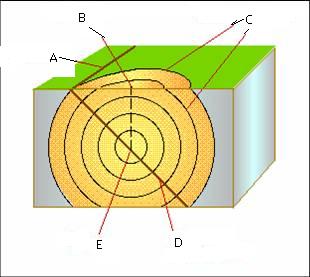 | E - The underground point of origin for an earthquake |
Epicenter,  | B - Point on the earth's surface directly above the focus |
| What is tension caused by? | Rocks being pulled apart |
| What are the 3 types of Stress | Compression, tension and shearing |
Normal Fault, 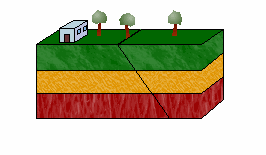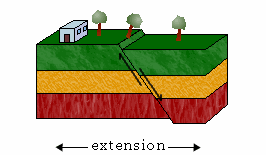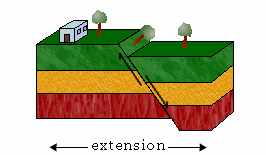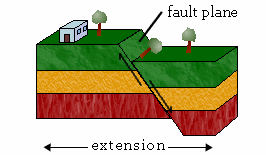 | Hanging wall moves down and foot wall moves up |
Reverse Fault, 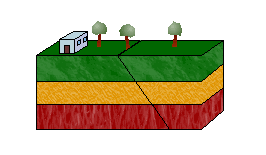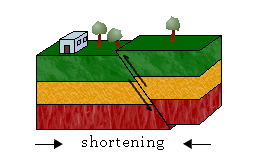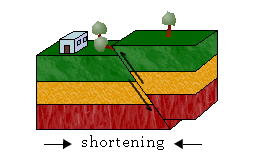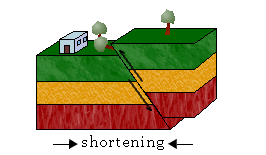 | Hanging wall moves up and foot wall moves down |
Lateral Fault/strike slip, 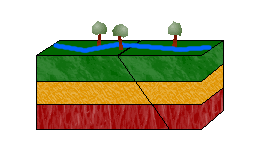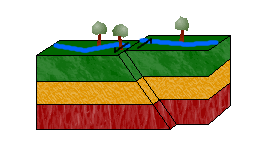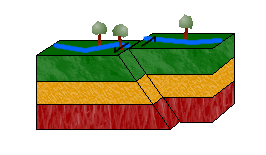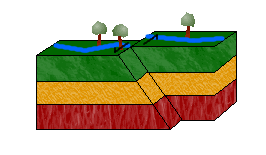 | Blocks of rock slide past each other - caused by shearing |
| Compression | Movement of rocks pressing together |
| Shearing | Movement of rocks sliding past each other laterally |
| Name 3 types of seismic waves | P waves, S waves & L waves |
| This wave travels the fastest | P waves |
| This wave moves only on the earth's surface | L waves |
| Waves that go through solids, liquids, & gases | P waves |
| Waves that travel from side to side | S waves |
| Waves that have a push pull motions | P waves |