| A | B |
|---|
| FDIC | Federal Depository Insurance Corporation |
| FDIC | Corporation that insures bank deposits up to $100,000 |
| Federal Reserve | Governmental agency in charge of banking and money control |
| The Fed | Short name for the Federal Reserve |
| Alan Greenspan | Current chair of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors |
| Ben Bernanke | Appointed to be the new chair of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors |
| Discount Rate | Short term interest rate set by the Fed for bank loans |
| Reserve Requirements | A percentage of demand deposits that banks must keep on deposit at the Fed |
| Open market operations | the buying and selling of U.S. Treasury Bonds (securities) to control money supply |
| Loose (expansionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that would increase the money supply |
| Loose (expansionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy normally pursued during a recessionary period |
| Loose (expansionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy normally pursued during a depressionary period |
| Loose (expansionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that might increase inflation |
| Loose (expansionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that should be pursued if GDP is decreasing |
| Loose (expansionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that should be implemented when unemployment is high |
| Tight (contractionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that would decrease the money supply |
| Tight (contractionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that would be pursued if inflation were high |
| Tight (contractionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that might cause a slowing of economic growth |
| Tight (contractionary) monetary policy | the type of monetary policy that might cause an increase in unemployment |
| CPI | stands for consumer price index - measures inflation |
| GDP | total value of all goods and services produced in the economy |
| Economic growth | an increase in real GDP |
| Inflation | an increase in the CPI |
| Above about 3% | inflation rate at which the Fed may implement a tight monetary policy |
| Full employment | an unemployment rate of 4% or lower is considered ________. |
| Above 5% | Unemployment rate at which the Fed may begin to loosen the money supply |
| Declining GDP | point at which the economy is contracting |
| Recession | declining GDP for 2 consecutive quarters |
| Depression | Severe, prolonged recession - high unemployment, declining GDP |
| How interest rates are determined | where demand for money intersects with the money supply |
| It is a fixed amount | why the money supply "curve" is a vertical line |
| Economic indicators | things the Fed looks at to determine the type of monetary policy to pursue |
| Functions of money | store of value, medium of exchange, measure of value |
| Monetary policy | the alteration of the money supply to try to ensure economic and price stability |
| Indicators that the Fed should contract the money supply | High inflation |
| Indicators that the Fed should expand the money supply | High unemployment, low or declining GDP |
| People's belief in it, the health of the economy | the things that "back up" money |
| Board of Governors | the governing body of the Federal Reserve |
| 12 | How many Federal Reserve districts there are |
| Aggregate Demand and Supply | Total demand and supply for all goods in our economy |
| Lower Reserve Requirements & Discount rate, Buy bonds | The three tools of the Fed and how they would be used to implement a loose monetary policy |
| Raise Reserve Requirements & Discount rate, sell bonds | The three tools of the Fed and how they would be used to implement a tight monetary policy |
| Aggregate demand increases | What happens when overall interest rates decline? |
| Aggregate demand decreases | What happens when overall interest rates increase? |
| Financial services of the Fed | check clearing, working as the nation's bank, maintaining the integrity of the money supply, consumer services |
| Banking supervision role of the Fed | Making rules and regulations that banks must follow, doing audits to protect consumers |
| Expansionary monetary policy |  |
| Contractionary monetary policy | 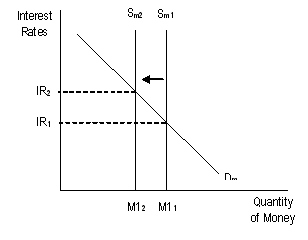 |
| Expansionary monetary policy would cause this effect | 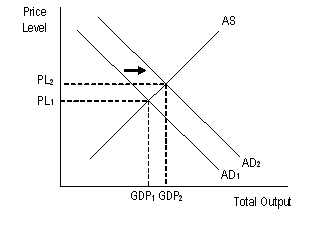 |
| Contractionary monetary policy would cause this effect | 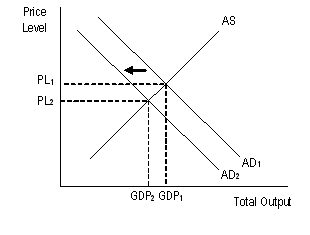 |