| A | B |
|---|
GREAT PLAINS,  | flatlands; eroded by wind and water; low rainfall; frequent dust storms |
| "TREELESS WASTELAND" | view of the Great Plains before Civil War |
| TECHNOLOGIES THAT HELPED SETTLE THE GREAT PLAINS | Barbed wire; steel plows; dry farming; sod houses; beef cattle raising; wheat farming |
| NEW ENGLAND | textile manufacturing area |
| DETROIT | center of the automobile industry |
| PITTSBURGH | center of the steel industry |
| 7 POLITICAL REGIONS OF THE U.S. | Northeast; Southeast; Midwest; Southwest; Rocky Mountain; Pacific; Noncontiguous |
NORTHEAST REGION, 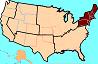 | Maine; Vermont; New Hampshire; |
SOUTHEAST REGION, 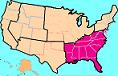 | Maryland; Delaware; West Virginia; Virginia; Kentucky; Tennessee; North Carolina; South Carolina; Georgia; Florida; Alabama; Mississippi; Louisiana; Arkansas |
MIDWEST REGION, 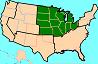 | Ohio; Indiana; Illinois; Michigan; Wisconsin; Minnesota; Iowa; Missouri; Kansas; Nebraska; South Dakota; North Dakota |
SOUTHWEST REGION, 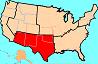 | Texas; Oklahoma; New Mexico; Arizona |
ROCKY MOUNTAIN REGION, 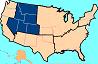 | Colorado; Utah; Nevada; Montana; Wyoming; Idaho |
PACIFIC REGION, 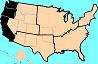 | Washington; Oregon; California |
| NONCONTIGUOUS STATES | Alaska; Hawaii |
| PHILADELPHIA, PITTSBURGH | Pennsylvania cities |
| BOSTON | city in Massachusetts |
| ATLANTA | city in Georgia |
| NEW ORLEANS | city in Louisiana |
| CHICAGO | city in Illinois |
| ST. LOUIS | city in Missouri |
| SANTA FE | city in New Mexico |
| SAN ANTONIO | city in Texas |
| SEATTLE | city in the state of Washington |
| SALT LAKE CITY | city in Utah |
| JUNEAU | city in Alaska |
| HONOLULU | city in Hawaii |
| SAN FRANCISCO & LOS ANGELES | California cities |
| DETROIT | city in Michigan |
| REASONS FOR WESTWARD EXPANSION | land ownership; transcontinental railroad; gold and silver; adventure |
| HOMESTEAD ACT | granted settlers free land on the Great Plains |
| LAND; A NEW BEGINNING | reason slaves moved west |
| WHY IMMIGRATION INCREASED AFTER THE CIVIL WAR | opportunities; adventure; religious freedom; escape from oppression |
| REASONS FOR THE GROWTH OF CITIES AFTER THE CIVIL WAR | immigration; migration from rural areas; specialized industries |
| CHICAGO | city that specialized in meat packing |
| THOMAS EDISON | inventor of electric lights |
ALEXANDER GRAHAM BELL,  | inventor – telephone communication |
| ELECTRICITY (LIGHTING); TELEPHONE SERVICE | inventions that led to industrial growth in the late 1800s |
| CHALLENGES FACED BY CITIES | overcrowded immigrant neighborhoods; tenements; political corruption |
| EFFORTS TO SOLVE IMMIGRATION PROBLEMS | settlement houses; political machines help with jobs and housing |
| JANE ADDAMS | founded Hull House, a settlement house to help immigrants |
| HOW POLITICAL MACHINES GAINED POWER IN THE CITIES | attended to the needs of new immigrants |
| RESERVATIONS | land set aside for Indian communities |
| FREQUENT SKIRMISHES, FIGHTING | interactions between Indians and whites in the mid-1800s |
| SIOUX | tribe led by Crazy Horse and Sitting Bull; fought General Custer at Little Big Horn |
LITTLE BIGHORN,  | Custer and his men all died in this famous battle against 2,000 Sioux Indians |
CHIEF JOSEPH,  | led Nez Perce Indians on a long trek to espcape reservation |
| CHINESE WORKERS | immigrants on the West Coast who were blamed for declining wages and economic problems |
| CHINESE | Congress tried to exclude these immigrants when it passed the first law restricting immigration |
| IRISH IMMIGRANTS | they poured into the U.S. in the 1840s after the potato crop failed |
| JIM CROW LAWS | legalized segregation |
| SEGREGATION | separation based on race |
BOOKER T. WASHINGTON,  | believed African American equality would come through education |
W.E.B. DU BOIS,  | wanted immediate equality for African Americans at any cost |
| BOOKER T. WASHINGTON VS. W.E.B. DU BOIS | one was willing to accept segregation temporarily; the other was not |
| AGRICULTURAL NATION BECAME INDUSTRIAL NATION | major economic transformation in U.S. between the Civil War and WWI |
| FACTORS THAT CAUSED THE RISE IN BIG BUSINESS IN THE LATE 1800S | national markets created by transportation advances; advertising; lower-cost production |
| "CAPTAINS OF INDUSTRY" | John D. Rockefeller (oil) Andrew Carnegie (steel), Henry Ford (cars) |
ROCKEFELLER’S BUSINESS,  | Standard Oil |
CARNEGIE’S BUSINESS,  | steel |
| ASSEMBLY LINE | technology used by Ford to make cars affordable |
| CAUSES OF INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE LATE 1800S | access to raw materials and energy; availability of work force; inventions; financial resources |
| RAILROADS, OIL, STEEL | big businesses that emerged after the Civil War |
THE REAPER,  | invention that allowed fewer men to harvest more wheat |
| CHANGES IN FARM LIFE AFTER THE CIVIL WAR | mechanization reduced farm labor needs and increased production; industrialization provided access to consumer goods by mail order |
| CITIES | where labor was needed during period of industrialization |
| EFFECT OF MECHANIZATION ON FARMS | increased productivity; fewer farm workers needed; laborers left farms for the cities |
| NEGATIVE AFFECTS OF INDUSTRIALIZATION | child labor; low wages and long hours; unsafe working conditions |
| PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WORKPLACE REFORMS | improved safety conditions; reduced work hours; restrictions on child labor |
| GOALS OF PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REFORMERS | laws to protect workers and poor people; government reforms; regulation of business |
| GOALS OF WOMEN'S SUFFRAGE MOVEMENT | voting rights; increased educational opportunities for women |
| THE AFL - AMERICAN FEDERATION OF LABOR | union that pushed for higher wages, shorter hours and better working conditions |
| AFL TACTICS | bargaining, not strikes; stronger in the skilled trades than the factories |
| HOMESTEAD STRIKE | strike at Carnegie's steel plant; 13 killed |
| RESULT OF THE HOMESTEAD STRIKE | Americans turned against unions and organized labor, which they blamed for the violence |
| 19TH AMENDMENT | gave women the right to vote |
| SUSAN B. ANTHONY | she fought for women's suffrage |
| 1920 | year 19th amendment adopted |
| TEMPERANCE MOVEMENT | movement against alcohol consumption and production |
| 18TH AMENDMENT | prohibited the manufacture, sale, and transport of alcoholic beverages |
| 1898 | year of the Spanish American War |
| CUBA (AND THE PHILIPPINES) | where Spanish American War was fought |
| SPANISH AMERICAN WAR | war that made American a world power |
| CAUSE OF THE SPANISH AMERICAN WAR | Cuban nationalists revolted against the Spanish government ruling Cuba |
| ORIGIN OF "YELLOW JOURNALISM" | reporters exaggerated Spanish atrocities in Cuba in order to sell newspapers |
| WHY AMERICANS SUPPORTED CUBAN REBELS | protection of American business interests in Cuba; exaggerated news reports about Spanish atrocities |
| THE U.S. BATTLESHIP MAINE | sunk by an explosion while off of the coast of Cuba. Spain unfairly blamed |
| RESULT OF THE SINKING OF THE MAINE | it gave America an excuse to declare war on Spain |
| PHILIPPINES, GUAM AND PUERTO RICO | new U.S. possessions from the Spanish American War |
| CUBA GAINED INDEPENDENCE FROM SPAIN | outcome of the Spanish American War for Cuba |
| 1914 | year World War I broke out in Europe |
| AMERICAN ATTITUDE TOWARDS WAR IN 1914 | isolationist policy; U.S. did not want to become involved in European conflicts |
| 1917 | year the U.S. entered WWI |
| WHY U.S. JOINED WAR IN EUROPE IN 1917 | German submarine warfare; sinking of Lusitania; U.S. economic and political ties to Great Britain |
| THE LUSITANIA | ship carrying Americans - sunk by a German sub during World War I prompting U.S. to enter the war |
| WORLD WAR I ALLIES | Great Britain; France; Russia; Serbia; Belgium |
| CENTRAL POWERS (WWI) | Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire (Turkey |
| LEAGUE OF NATIONS | President Woodrow Wilson idea for keeping the peace |
| U.S. CONGRESS | rejected U.S. participation in the League of Nations |
| WHY CONGRESS REJECTED THE LEAGUE OF NATIONS | preferred isolationist policy of the past; did not want us tangled up in world affairs |
| CHANGE IN 20TH CENTURY AMERICAN LIFE | technology – it extended into all areas of American life, even in rural areas |
| TECHNOLOGIES THAT CHANGED AMERICAN LIFE IN THE EARLY 1900S | affordable autos; airplane; assembly line; telephone; radio; movies; electrification; labor saving home products |
| WRIGHT BROTHERS | inventors of the airplane |
| CHANGES BROUGHT BY THE AUTOMOBILE | mobility; jobs; new industries; road construction; suburbs |
| EFFECTS OF ELECTRIFICATION | labor-saving products; washing machine, electric stove, water pumps; electric lighting; radio for entertainment |
RADIO DEVELOPER,  | Guglielmo Marconi |
DAVID SARNOFF,  | broadcast industry developer |
PROHIBITION,  | a constitutional amendment made it illegal to manufacture, transport and sell alcoholic beverages |
| LESSON LEARNED FROM PROHIBITION | It is difficult to legislate how people behave. |
| UNINTENDED RESULTS OF PROHIBITION | speakeasies; bootleggers; organized crime. |
| SPEAKEASIES | places to drink alcoholic during Prohibition |
| BOOTLEGGERS | smuggled illegal alcohol and promoted organized crime |
GREAT MIGRATION NORTH,  | African Americans migrated to northern cities, leaving the South where jobs were low-paying and scarce |