| A | B |
|---|
| HARLEM RENAISSANCE | movement of African American artists, writers, musicians in Harlem |
JACOB LAWRENCE,  | Harlem Renaissance painter - showed Great Migration north |
LANGSTON HUGHES,  | Harlem Renaissance poet |
ELLINGTON AND ARMSTRONG,  | Harlem Renaissance jazz composers |
| BESSIE SMITH | Harlem Renaissance blues singer |
GEORGIA O'KEEFFE,  | Artist known for urban scenes and paintings of flowers and the Southwest |
F. SCOTT FITZGERALD,  | He wrote novels about the Jazz Age of the 1920s |
JOHN STEINBECK,  | Author of Grapes of Wrath, a novel about poor migrant worker during the 1930s |
| AARON COPLAND AND GEORGE GERSHWIN | Uniquely American composers of the 1920s and 1930s |
| CAUSE OF GREAT DEPRESSION | overspeculation on stocks with borrowed money |
| HIGH TARIFFS | strangled international trade contributing to Great Depression |
| IMPACT OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION | one fourth of workers without jobs; banks and businesses failed; people were hungry and homeless; farm income fell |
| NEW DEAL | Roosevelt's plan to use government programs to help the nation recover from the Depression |
| FEATURES OF THE NEW DEAL | social security; federal work programs; environmental improvement programs; farm assistance programs; increased rights for labor |
| POST WWI CONDITIONS IN EUROPE | Depression, high inflation, massive unemployment, Germany - huge war debt |
| FASCISM | Political philosophy- total power to dictator, individual freedoms denied |
| 3 FASCIST DICTATORS | Hiter (Germany), Mussolini (Italy), Tojo (Japan) |
| NEUTRALITY; ISOLATIONISM | America's foreign policy when WWII began |
| HOW U.S. FOREIGN POLICY EVOLVED DURING WWII | From isolationism to economic aid to direct military involvement |
| WWII ALLIES | U.S., Great Britain, Canada, the Soviet Union (after German invasion) |
| U.S. PRESIDENTS DURING WWII | FDR (Franlin D. Roosevelt); Harry Truman in 1945 after FDR's death |
| AXIS POWERS | Germany, Italy, Japan |
| DECEMBER 7, 1941 | Date of Pearl Harbor attack |
WINSTON CHURCHILL,  | WWII leader of Great Britain |
PEARL HARBOR,  | Resulted in U.S. military involvement in WWII |
STARTED WWII,  | Hiter's invasion of Poland |
| DATE HITLER BEGAN INVASION OF POLAND | September 1, 1939 |
| GERMANY, THE SOVIET UNION | These two countries divided Poland in half |
| PARIS, FRANCE | A year after invading Poland, German troops marched victoriously into this European capital |
BATTLE OF BRITAIN, 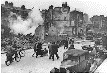 | In 1940, Germans bombed British cities in this battle |
| THE SOVIET UNION | Hitler invades this old ally in June, 1941 |
BATTLE OF MIDWAY,  | Turning point in the Pacific |
BATTLE OF STALINGRAD,  | Turning point in the war in Eastern Europe |
NORMANDY, FRANCE,  | D-day landing took place here |
| BOMBING OF HIROSHIMA AND NAGASAKI | Ended WWII,  |
| GENOCIDE | Wiping out of an entire race |
| THE HOLOCAUST | Hitler's effort to annihilate Jews |
| CONCENTRATION CAMPS | Prison camps for Jews and others |
| ANTI-SEMITISM | Hatred of Jews |
| ARYAN SUPREMACY | Notion that Germans are a superior race |