| A | B |
|---|
| A CELL | What is the basic unit of all living things? |
| All living things are composed of cells; cells are the smallest unit of living things that can perform the functions necessary for life; living cells come only from other living cells. | What is the cell theory? |
THE MICROSCOPE,  | What is the invention that made it possible to see cells? |
| interphase, mitosis, cytokineses | What are the stages of the cell cycle? |
| mitosis and meiosis | What are two kinds of cell division? |
THE NUCLEUS, 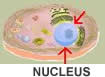 | What structure acts as the cell's control center? |
CELL WALL, 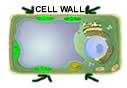 | What is the rigid outer layer of plant cell? |
CYTOPLASM, 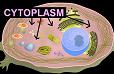 | What is the jelly-like substance in a cell that contains organelles? |
CHLOROPLAST,  | What part of a plant cell changes the sun's energy to food? |
VACUOLE,  | What organelle stores food, water and waste? |
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM, 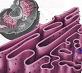 | What organelle is a folded membrane that moves things around a cell? |
| PLANT CELL | What kind of cell has chloroplasts and a cell wall? |
| ANIMAL CELL | What kind of cell does not have a cell wall or chloroplasts? |
MITOCHONDRION,  | What organelle acts as the cell's "powerhouse" by releasing energy from food? |
| GOLGI BODIES | What organelle packages and moves proteins out of cell? |
| ORGANELLES | What are the structures within the cytoplasm called? |
CELL MEMBRANE,  | What allows materials into and out of the cell? |
| RIBOSOMES | What organelle makes proteins and is located in the cytoplasm or attached to the ER? |
MITOSIS, 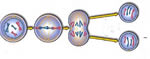 | What kind of cell reproduction produces two identical daughter cells? |
MEIOSIS, 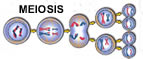 | What kind of reproduction produces cells with half the number of chromosomes? |
INTERPHASE,  | What is the period of cell growth and development called? |
| CYTOKINESIS | What do you call the division of the cytoplasm after mitosis? |