| A | B |
|---|
| The repeating building blocks of larger molecules are known as ____. | monomers |
| Many monomers linked together make up a ____. | polymer |
| A polymer is a large molecule made up of many ____. | monomers |
| The root word "poly" means ____. | many |
| The root word "mono" means ___. | one |
| The four categories of biological macromolecules are ___, ___, ___, and ___. | carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, 
|
| The type of macromolecule that is used primarily as a source of quick energy is ___. | carbohydrates, 
|
| Bread, pasta, cereal and fruits are high in which type of macromolecule? | carbohydrates, 
|
| The monomers of complex carbohydrates are ___. | simple sugars (a.k.a. monosaccharides), 
|
| Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of ____. | simple sugars (or monosaccharides - note; these three are all hexose sugars meaning they have six carbons. There are also simple sugars that are pentose sugars with 5 carbons such as ribose and deoxyribose, found in nucleotides. Triose sugars such as glycerodehyde are important in respiration and photosynthesis), 
|
| Sucrose is commonly called ____. | table sugar |
| Sucrose is a type of carbohydrate made of glucose bonded to fructose. Therefore, it is a ___. | disaccharide |
| Another term for simple sugars is ___. | monosaccharides, 
|
| Many monosaccharides bonded together are called a ____. | polysaccharide, 
|
| Lactose is a type of disaccharide found in _____. | milk |
Plants usually store their carbohydrates as the polysaccharide known as ____., 
| starch |
Animals store carbohydrates in their liver and muscles as the polysaccharide known as ___., 
| glycogen, 
|
| The cell walls of plants are made of the polysaccharide known as ____. | cellulose,  , , 
|
| ____ is a tough polysaccharide that can only be broken down by bacteria and some types of fungi. | cellulose,  |
Cellulose in plant cell walls can only be broken down for energy by ___ ., 
| bacteria and certain fungi (Animals that eat grass, which is mostly cellulose, depend on bacteria in their digestive tract to break the cellulose down into sugar monomers that the animals can then digest. Often times, there will be a compartment in their digestive tract that is sectioned off for this purpose),  |
Glycogen is mainly stored in an animals ___ and ____., 
| muscles and liver |
Starch, glycogen and cellulose are all types of ___., 
| carbohydrates, 
|
| Sugars are classified as ___. | carbohydrates, 
|
| The monomers of proteins are ____. | amino acids, 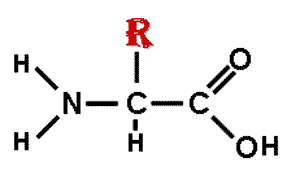 , , 
|
A long straight chain of amino acids is called a ____., 
| polypeptide, 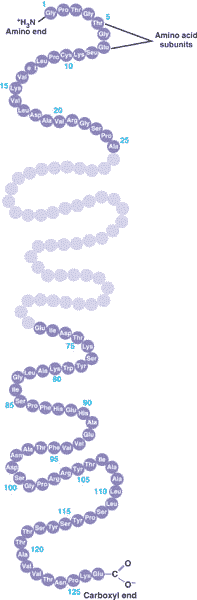 |
A polypeptide that folds into a 3-D structure that has a specific function is called a ___., 
| protein (The picture below shows the different bonds that hold the protein in its folded shape), 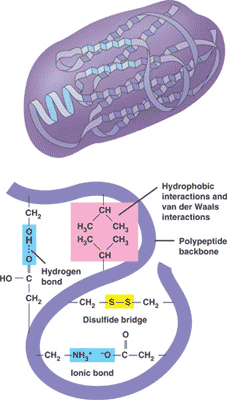 |
Lean meat is highest in the macromolecule known as ____., 
| protein |
| A protein whose shape has been changed due to heat or harsh chemicals is known as a ____ protein. | denatured |
Organic catalysts are known as ___., 
| enzymes, 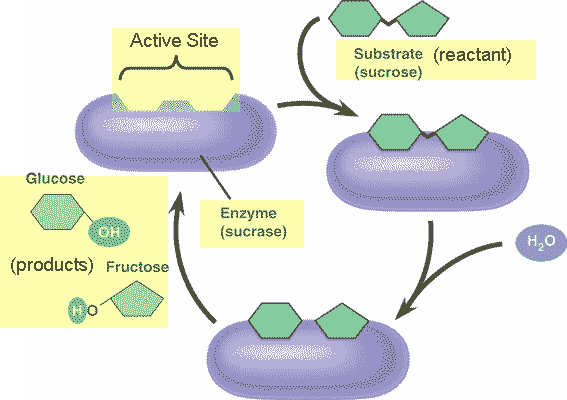 |
| An enzyme ____ a chemical reaction. | speeds up,  |
| DNA and RNA are types of ____. | nucleic acids, 
|
| The type of molecule that holds an organism's genetic information is called ___ and belongs in the class of macromolecules known as ____. | DNA, nucleic acids,  |
| The monomers of nucleic acids are ____. | nucleotides,  , , 
|
| DNA is made up of four different types of ____. | nucleotides (Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are the nucleotides in DNA. In RNA, uracil is substituted for thymine. The picture below shows the nitrogenous bases of each which give the nucleotides their names), 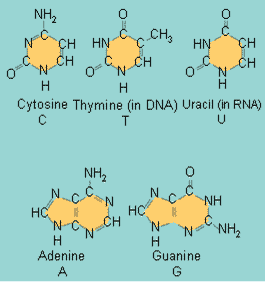 |
| Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are ____ found in ____. | nucleotides, DNA,  |
The order of nucleotides in DNA determines the order of ____ in a protein., 
| amino acids,  , , 
|
A change in the order of nucleotides in DNA is known as a ____., 
| mutation |
A type of nucleic acid that is single-stranded is ___., 
| RNA |
A type of nucleic acid that is double stranded is ___., 
| DNA |
| Fats, cholesterol, steroids and waxes are classified as ___. | lipids |
| The main function of lipids in an animals body is to ____. | store energy for later use |
| Red meats, dairy and fried foods are high in the type of macromolecules known as ___. | lipids |
| The building blocks of fats are ___ . | Three fatty acids and one glycerol (The picture below shows a glycerol shaded gray and one long fatty acid chain shaded orange),  |
| Besides being used to store energy, lipids are also used for ___. | Insulation, protecting internal organs, material to making cell membranes and some hormones. |
| Fats that are solid at room temperature and are not particularly good for you are a type called ___. | saturated fats,  |
| Fats that are liquid at room temperature and are considered healthy to eat are called ___. | unsaturated fats,  |
| ____ are high in saturated fats. | Red meats |
| Fats from vegetable oils and fish tend to be ___. | unsaturated,  |
| Phospholipids are major component of the ___. | cell membrane,  |
| A major component of cell membranes is a type of lipid called a(n) ___. | phospholipid, 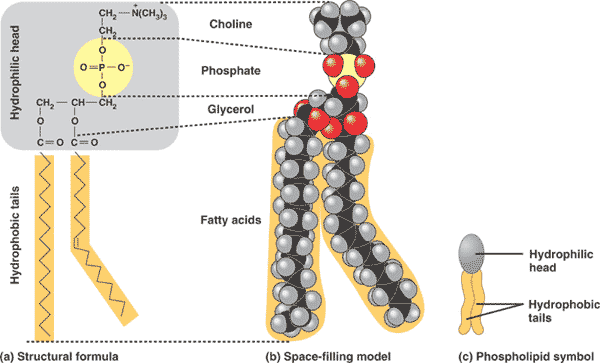 |
Enzymes are almost always made of ____., 
| proteins |
The chemical or chemicals that an enzyme works on is called the ___., 
| substrate,  |
| The part of the enzyme that the substrate fits into is called the ___. | active site,  |
The picture below shows a _______ structure called a(n) ________.,  | secondary structure, alpha helix (keratin, a structural protein in hair and fingernails has alpha helix structure over most of its length),  |
The picture below shows the base structure of a(n) ______.,  | amino acid,  |
| Draw the base structure of an amino acid and use an R to signify the radical group (where amino acids become different). | .,  |
The picture below shows a _______ structure called a(n) ________., 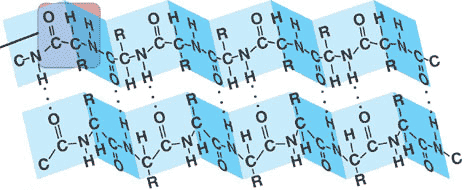 | secondary structure, beta pleated sheet (this structure is found at the core of many globular proteins and in some fibrous proteins such as spider silk),  |
The picture below shows the structure of _____., 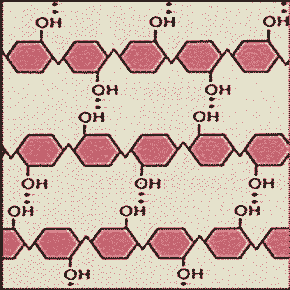 | cellulose (Cellulose is a tough structural carbohydrate which is impossible to digest, unless you are a bacterium or a fungus, due to the cross-linked bonds that hold the chains together side-by-side),  |
What is the structure that is helping the polypeptide fold into a protein?, 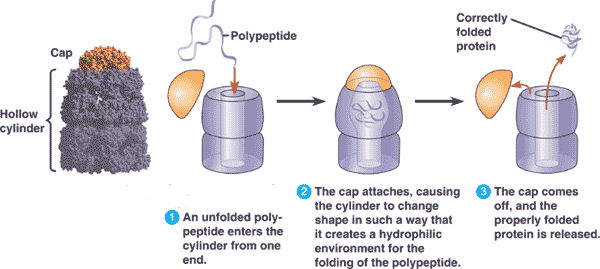 | A chaperonin (which is itself made of protein),  |
What is the exoskeleton made of that the insect below is trying to molt out of?,  | chitin (Which is a type of structural carbohydrate. It also makes up the exoskeleton of crustaceans like lobster and crab that are closely related to insects),  |
The picture is showing a _____ reaction.,  | condensation reaction (a.k.a. - dehydration synthesis),  |
| Another name for dehydration synthesis is _____. | condensation reaction,  |
The picture below is showing part of a molecule of _____ which has a ______ shape.,  | DNA, double helix,  |
Where is the active site in this picture?, 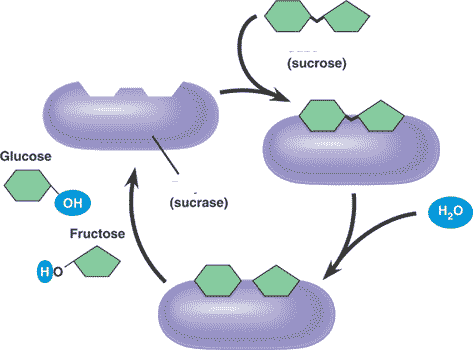 | .,  |
| The monomers of maltose are _______. | glucose and glucose |
| The monomers of sucrose are ___. | glucose and fructose |
| The monomers of lactose are ____. | glucose and galactose |
Glucose and fructose bond to form a _____ called _____., 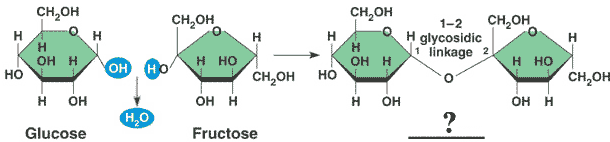 | disaccharide called sucrose (table sugar),  |
Glucose and glucose bond to form a _____ called _____., 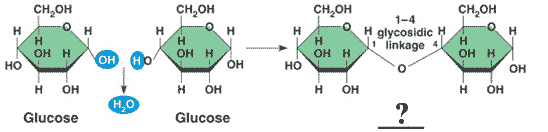 | disaccharide called maltose (malt sugar),  |
| Glucose and galactose bond to form a _______ called _____. | disaccharide called lactose (milk sugar) |
What is the product of this reaction?,  | glucose and fructose,  |
What is the reactant of this reaction?,  | sucrose,  |
What is the name of the enzyme in this reaction?,  | sucrase (notice how it's named after the substrate it breaks down),  |
Why is water needed for this reaction?,  | Its a hydrolysis reaction (the water is needed to break the bond between the glucose and fructose that make up the sucrose),  |
| Glucose alternates back and forth between a _____ structure and a ______ structure. | straight chain (linear) structure and a ring structure,  |
| Fat is a type of _____ that is made of _____ and _____. | lipid, 1 molecule of glycerol and three fatty acid chains (This picture shows how one glycerol would bond through a condensation reaction to one molecule of fatty acid),  |
The reaction shown below is called a(n) _____ reaction.,  | hydrolysis,  |
| A nucleotide is made of _____. | a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base,  |
| A nucleoside is made of _______. | A pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base (not the phosphate group),  |
What is "A" pointing out?, 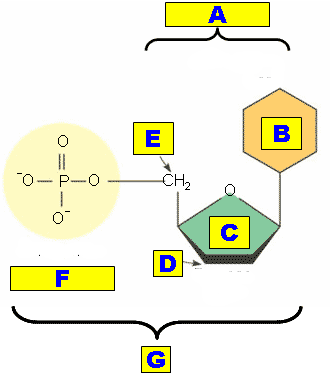 | The nucleoside part of a nucleotide,  |
What is "B" pointing out?,  | The nitrogenous base part of a nucleotide,  |
What is "C" pointing out?,  | The pentose sugar part of a nucleotide,  |
What is "D" pointing out?,  | The #3 carbon part of a nucleotide,  |
What is "E" pointing out?,  | The #5 carbon part of a nucleotide,  |
What is "F" pointing out?,  | The phosphate part of a nucleotide,  |
What is "G" pointing out?,  | An entire nucleotide,  |
What is this and what is it made of?,  | Part of a cell membrane showing a lipid bilayer made of phospholipids |
Where do you find this type of molecule?,  | cell membranes |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein.,  | primary structure,  |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein., 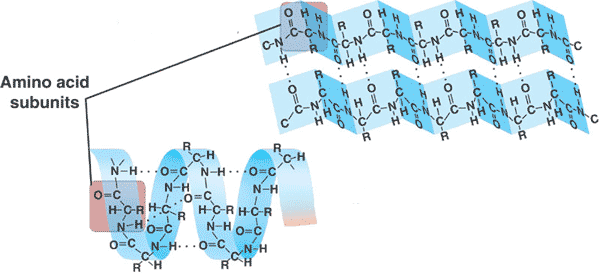 | secondary structure |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein.,  | tertiary structure |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein., 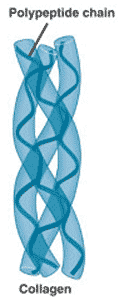 | quarternary structure (notice how the collagen protein, which is a major component of connective tissue, has 3 proteins that form a braid. The alpha-helix structure of the individual proteins give collagen its rubber band-like stretchy characteristics. Old people lose that elasticity in their collagen, leading to wrinkled skin),  |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein., 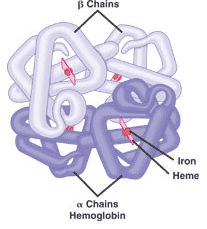 | quarternary structure (This hemoglobin protein is made up of four intertwining polypeptide chains. As the oxygen carrying molecule in red blood cells, hemoglobin also has 4 heme groups with iron at the center to bind directly to oxygen) |
"A" is pointing to ____ in this picture showing _____.,  | DNA, protein synthesis,  |
"B" is pointing to ____ in this picture showing _____.,  | m-RNA (messenger RNA) after it has been transcribed from the DNA template, protein synthesis,  |
"C" is pointing to ____ in this picture showing _____.,  | m-RNA (messenger RNA) after it has left the nucleus in search of a ribosome, protein synthesis,  |
"D" is pointing to ____ in this picture showing _____.,  | aribosome, protein synthesis,  |
"E" is pointing to ____ in this picture showing _____.,  | a polypeptide chain, protein synthesis,  |
"F" is pointing to ____ in this picture showing _____.,  | amino acids, protein synthesis,  |
All of these molecules are _____. The smaller ones in the top row are called _____.,  | nitrogenous bases, pyrimidines),  |
All of these molecules are _____. The larger ones in the bottom row are called _____.,  | nitrogenous bases, purines,  |
The molecule on the top is a(n) ______ while the molecule on the bottom is a(n) ____., 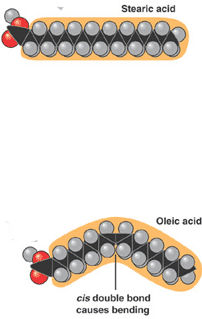 | saturated fatty acid (top), unsaturated fatty acid (bottom),  |
This picture depicts _____.,  | secondary structure of proteins |
Lipids with a ring structure are called _____., 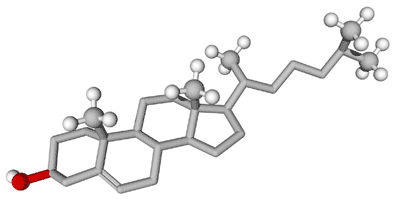 | steroids (cholesterol as well as testosterone are steroids),  |
| _____ fats increase the risk of __________ by increasing your bodies own production of ______. | Saturated fats increase the risk of atherosclerosis (heart disease) by increasing your bodies own production of cholesterol. |
| Hydrogenated vegetable oils are _____ that have been converted into ____ by synthetically adding hydrogens. | unsaturated fats into saturated fats (and also trans fats which may be even worse than saturated fats) |
| Atherosclerosis (heart disease) is characterized by the build up of deposits called _____ on the inside walls of blood vessels that can block blood flow. | plaques |
The picture below shows a molecule of _____ which is made of ____ bonded to _____.,  | fat (a.k.a. - a triglyceride), made of glycerol bonded to three fattly acids,  |
| Cystein is an amino acid with a sulfhydryl group as part of its R group. When a protein is folding, two cysteins from different parts of the polypeptide may bond at the sulfhydryl site to form a _______. | disulfide bridge,  |
| which macromolecule stores more than twice as much energy per gram compared to the other categories? | Lipids have about 9 kcalories per gram compared with 4 for carbohydrates and proteins |
| What is the molecular formula of a hexose sugar such as glucose? | C6H1206 (fructose and galactose have the same molecular formula as glucose. Therefore, all three are isomers) |
| What is the molecular formula of a disaccharide? | C12H22O11 (When two hexose sugars with molecular formulas of C6H12O6 come together, you have to subtract out 2 hydrogens and one oxygen that are lost as water from the dehydration synthesis reaction) |