| A | B |
|---|
| The process by which cells become specialized in structure and function is called ________. | cell differentiation |
| The physical processes that give an organism its shape constitute _________. | morphogenesis |
| ____________ events lay out the basic body plan very early in embryonic development, establishing, for example, which end of an animal embryo will be the head, or which end of a plant embryo will become the roots. | Morphogenetic |
| The end of an animal that is near the head is called the _______ end. | anterior |
| The end of an animal that is near the tail is called the _______ end. | posterior |
| The belly of an animal is said to be on the ______ side of the body. | ventral |
| The back of an animal is said to be on the ______ side of the body. | dorsal |
| A major difference between the development of plants and animals is that animals require ______. | movement of cells and tissues during development |
| A major difference between the development of plants and animals is that in plants, ______. | growth and morphogenesis occur throughout the life of a plant |
| The structures found on the tips of shoots and roots in plants that are responsible for a plant's continual growth and formation of new organs are called _______. | apical meristems,  |
| Any cell that is still capable of differentiating into any of the specialized cell types of the mature organisms is said to be _______. | totipotent |
| Using one or more somatic cells from a multicellular organism to make another genetically identical individual is called _____. | cloning |
| ________ cells are cells that are relatively unspecialized that can reproduce indefinitely and are capable of differentiating into one or more specialized cell types. | Stem cells,  |
| Totipotent stem cells can be isolated from early human embryos at the _______ stage of development. | blastocyst (The blastula stage in the picture below is how the blastocyst stage is characterized in non-human animals), 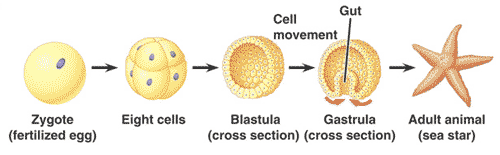 |
| Adult stem cells are said to be _______ because they can give rise to multiple, but not all cell types. | pluripotent,  |
| When the major aim of cloning is to produce embryonic stem cells to treat disease, the process is called _________. | therapeutic cloning |
| Maternal substances in the egg that influence the course of early development are called ___________. | cytoplasmic determinants |
| What are the two sources of information that tell a cell which genes to express at any given time during embryonic development? | 1) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. 2) Induction by nearby cells., 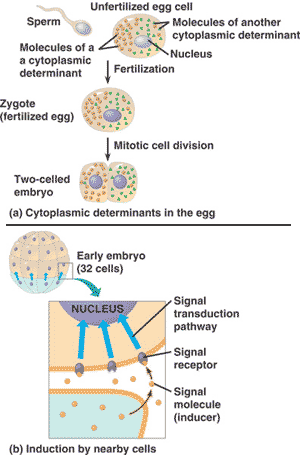 |
| Even before fertilization in Drosophila, neighboring nurse cells cause localization of _______ mRNA at one end of the egg, thus helping to establish the anterior end of the future embryo. | bicoid, 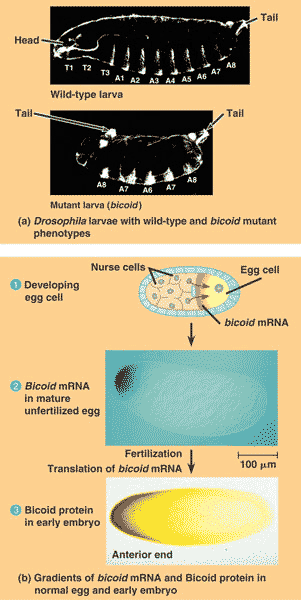 |
| It is _________ (the signaling from one group of cells to an adjacent group) that brings about differentiation. | induction |
| In Drosophila, _________ is an example of a cytoplasmic determinant. | bicoid mRNA,  |
| In Drosophila, bicoid mRNA is an example of a __________. | cytoplasmic determinant,  |
| During development, certain cells are meant to die instead of divide. This programmed cell death is called ______. | apoptosis |
| "Evo-devo" stands for _____. | evolutionary developmental biology |
Which process is responsible for the separation of the digits in this developing mouse paw?, 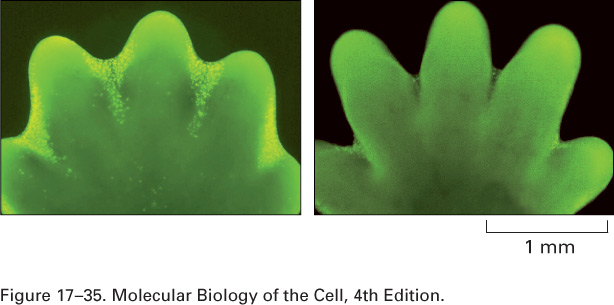 | Apoptosis (programmed cell death - in this case, the cells between the digits die, causing the separation), 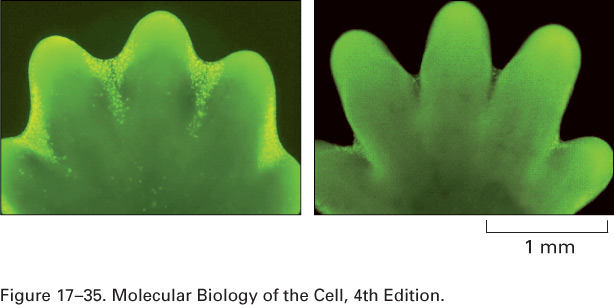 |
| Plant homeotic genes that use positional information to determine which emerging leaves develop into which types of floral organs are called _____. | organ identity genes |
| The ordering of cells into specific three-dimensional structures, critical for shaping an organism and its individual parts during development, is called _____. | pattern formation |
| Another name for a maternal effect gene (a gene that helps control the orientation of the egg). | egg-polarity gene |
| A gene that, when mutant in the mother, results in a mutant phenotype in the offspring, regardless of the offspring's genotype. | maternal effect gene |
| An organism with a mixture of genetically different cells is called a(n) ________. | chimera (named after the mythical creature that has parts of different animals, including humans, for its body) |
| The progressive restriction of developmental potential, causing the possible fate of each cell to become more limited as the embryo develops. | determination |
| A mutation with a phenotype leading to death at the embryo or larval stage is called a(n) ______. | embryonic lethal |
| Any of the genes that control the overall body plan of animals and plants by controlling the developmental fate of a group of cells is called a(n) ______. | homeotic gene |
| Signals to which genes regulating development respond, indicating a cell's location relative to other cells in an embryonic structure. | positional information |
| A 180-nucleotide sequence within homeotic genes and some other developmental genes that is widely conserved in animals. Related sequences occur in plants and prokaryotes. | homeobox |
| A gene of the embryo that directs the actual formation of segments after the embryo's axes are defined. | segmentation gene |
| A substance, such as Bicoid protein, that provides positional information in the form of a concentration gradient along an embryonic axis. | morphogen |