| A | B |
|---|
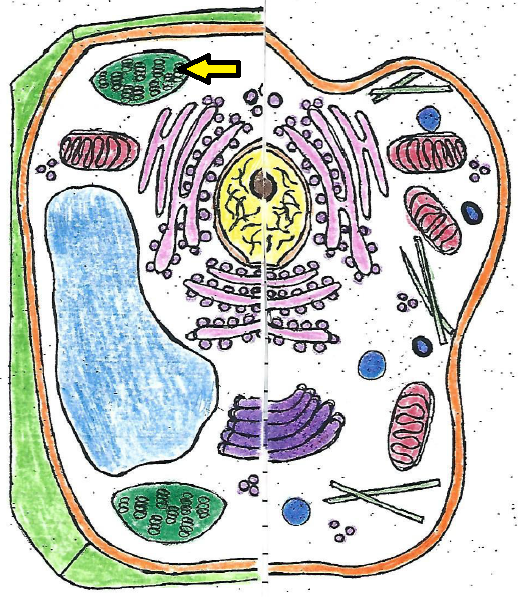 | chloroplast |
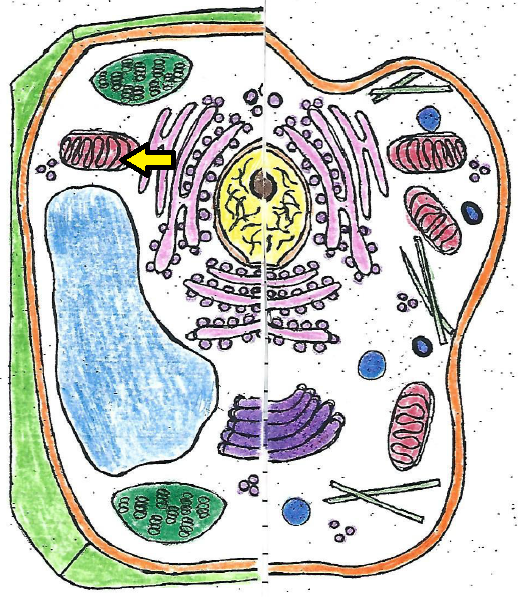 | mitochondria |
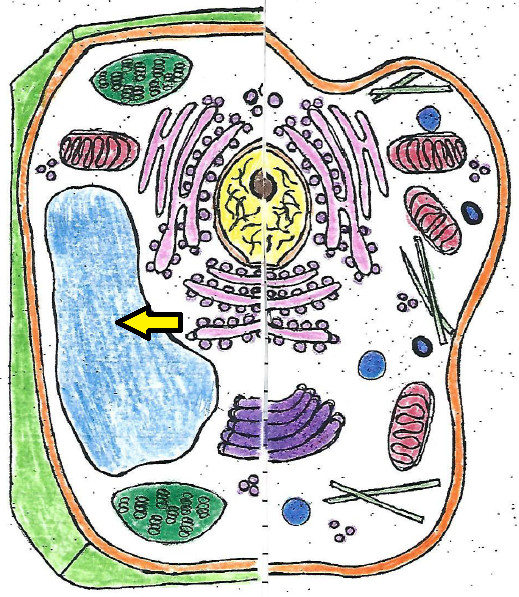 | vacuole |
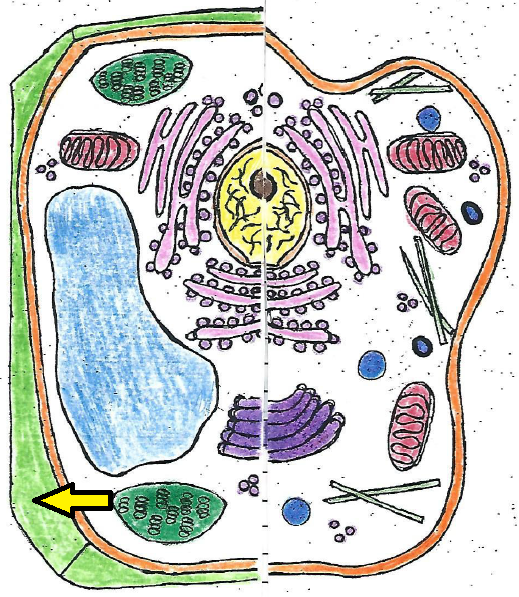 | cell wall |
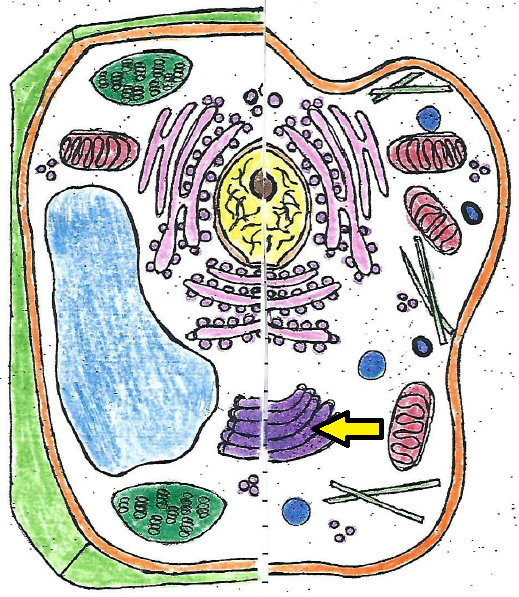 | Golgi Body |
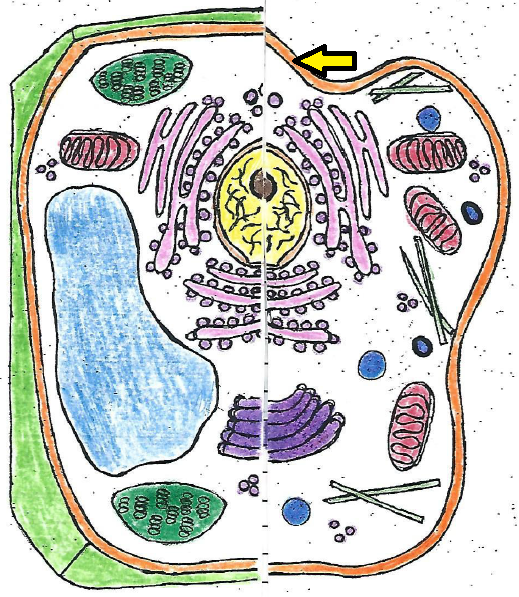 | cell membrane |
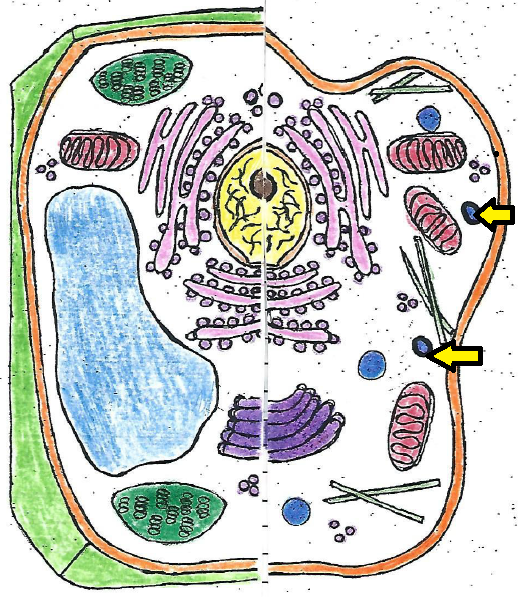 | lysosome |
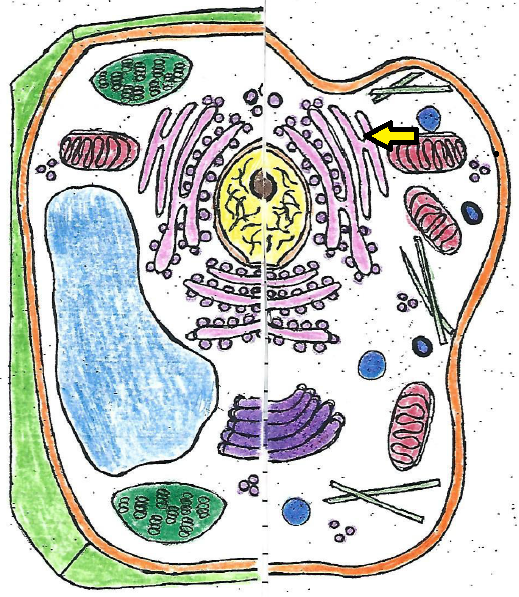 | endoplasmic reticulum |
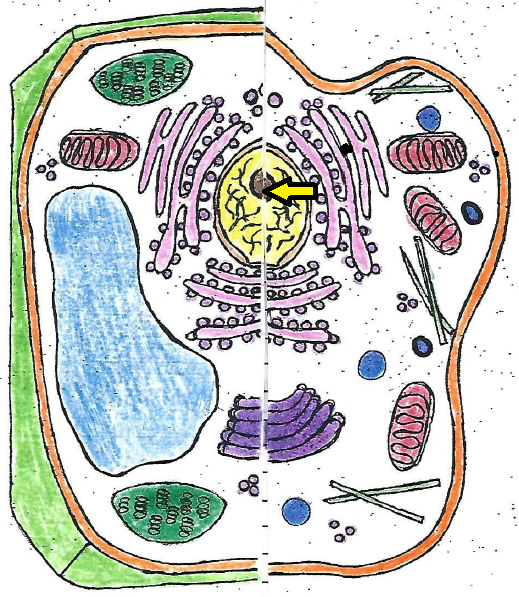 | nucleolus |
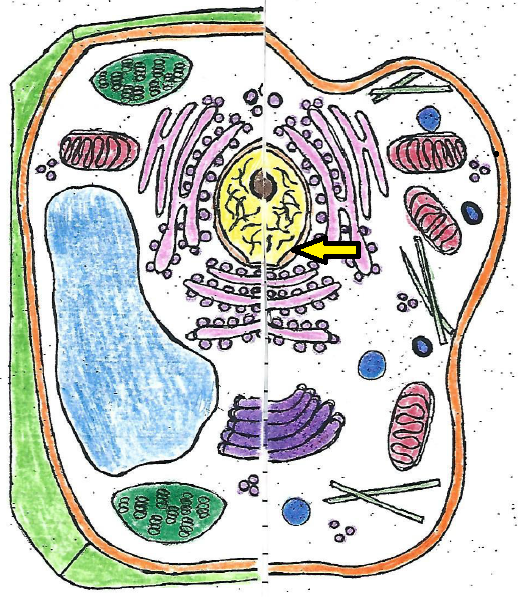 | nuclear membrane |
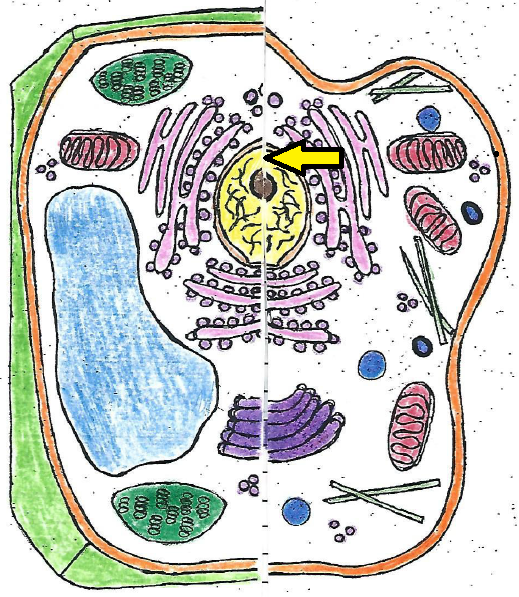 | nucleus |
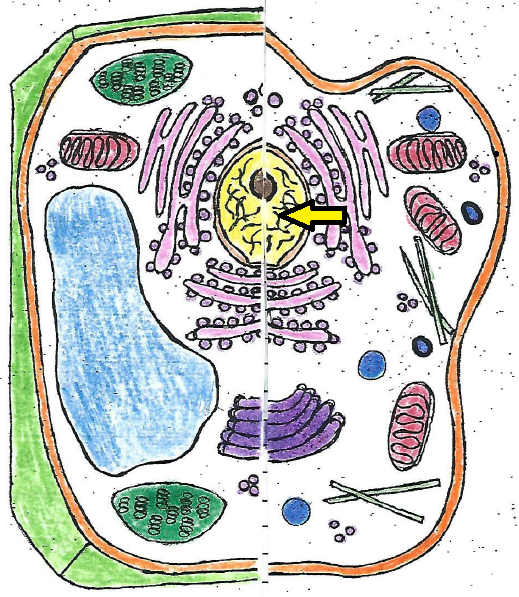 | chromatin |
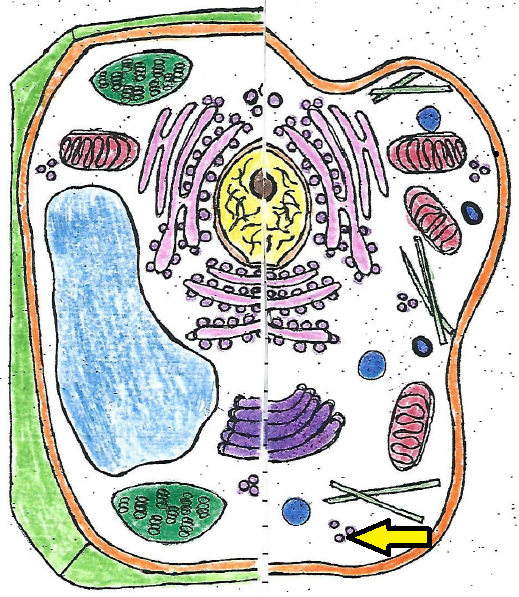 | ribosome |
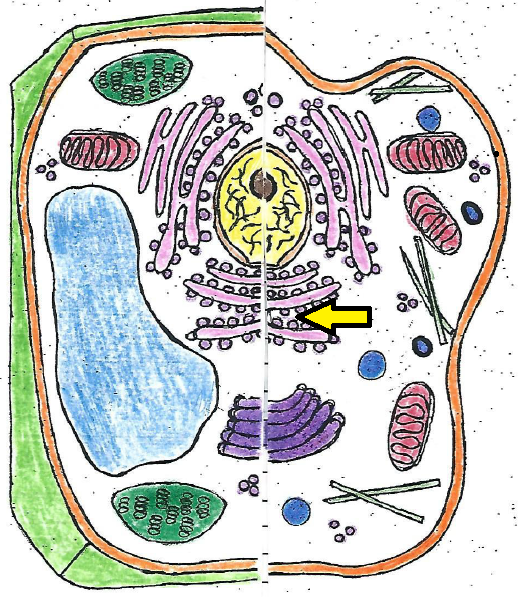 | ribosome |
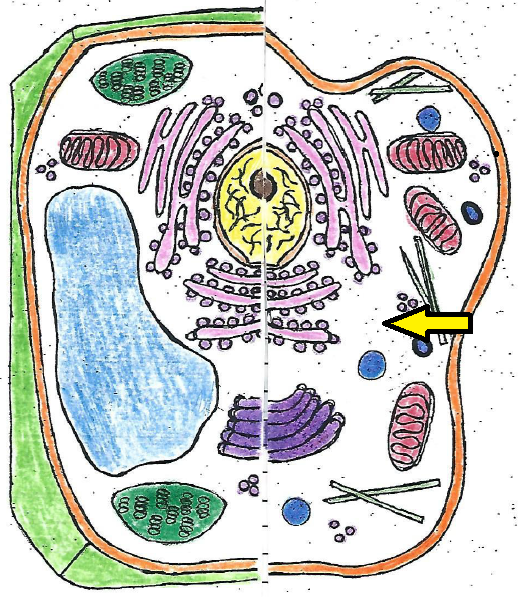 | cytoplasm |
| chloroplast | converts energy from the sun into chemical energy for plant cells |
| mitochondria | provides energy from cell; often known as the powerhouse |
| vacuole | stores water, food, and waste products |
| cell wall | provides support and protection for a plant cell |
| Golgi Body | receives proteins from the ER and packages and distributes proteins to other parts of the cell |
| cell membrane | regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell |
| lysosome | contains chemicals that break down food and other cell parts |
| endoplasmic reticulum | a series of tubes or passages throughout the cell that carry materials and package protein |
| nucleolus | found in the nucleus, stores materials to be used by other organelles |
| nuclear membrane | a thin membrane with many pores that surrounds the nucleus |
| nucleus | acts as the control center, directing all of the cell's activities |
| chromatin | found inside the nucleus, contains proteins, RNA, and DNA |
| ribosomes | small structures that function as factories for proteins |
| cytoplasm | jelly-like substance inside the cell that surrounds the organelles |