|
The major steps of the Kreb's Cycle are highlighted
over the next few pages. Believe it or not, there are actually many
more intermediary steps but for the sake of simplicity, we will
stick with the major steps.
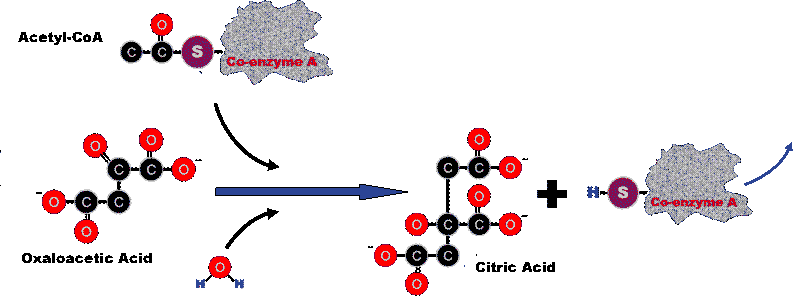
Step 1: Acetyl-CoA from
the transition phase enters the Kreb's Cycle by combining with oxaloacetic
acid to form a 6-carbon molecule called citryl-CoA. The citryl-CoA
then reacts with water, and releases the Coenzyme A to form citric
acid. Coenzyme A is then free to go back and escort another acetyl
group into the cycle. If the mitochondria is low on oxaloacetic
acid and acetyl-CoA accumulates as it waits to enter the cycle,
the excess acetyl-CoA can actually stimulate an enzyme called pyruvate
carboxylase which converts pyruvate to oxaloacetic acid.
|
|
|
