|
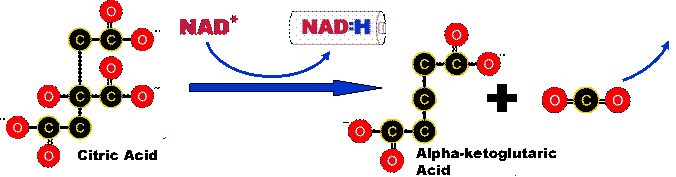
Step 2: There are actually
several intermediary steps to get from citric acid to alpha-ketoglutaric
acid. The end result is that a carbon dioxide molecule is removed
turning the six carbon molecule into a five carbon molecule. In
the process, a NAD+ is reduced to NADH and will carry the hydrogen
and the pair of high energy electrons to the electron transport
chain.
The more detailed version of this reaction involves
a dehydration of citric acid to form cis-aconic acid and then a
condensation reaction to form isocitric acid (an isomer of citric
acid). The enzyme responsible is aconitase. Then the isocitric acid
is oxidized by NAD+ to form oxalosuccinic acid before being decarboxylated
(having carbon removed) to form alpha-ketoglutaric acid. The enzyme
responsible is isocitrate dehydrogenase.
|
|
|
