|
Once inside the
matrix, a complex series of reactions unfold as summarized below.
These reactions are catalyzed by a large multienzyme complex referred
to in general as pyruvate dehydrogenase.
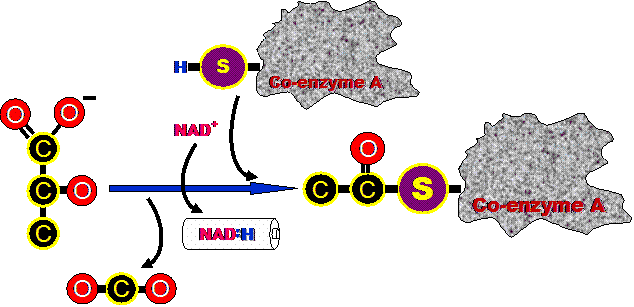
One carbon and two oxygens are removed from the pyruvate. These
atoms leave the mitochondria as carbon dioxide. The 2-carbon molecule
that is left over is basically acetic acid.
Electrons and hydrogen are transferred from the acetic acid to
NAD+ as the NAD+ is reduced to NADH. NADH carries those electrons
and hydrogen to the electron transport chain.
Coenzyme A attaches to the acetic acid to form a molecule called
acetyl CoA. Coenzyme A then carries the acetyl group over to the
entry point of the next phase called the Kreb's Cycle.
|
|
|