|
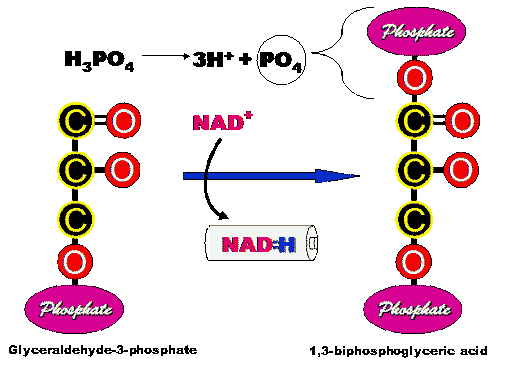
Step 5: In this step,
each molecule of PGAL gives up a hydrogen and two high energy electrons
to the hydrogen accepting molecule known as NAD+. The resulting
molecule, NADH, will carry these high energy electrons to the electron
transport chain which you will learn about later on.  The reaction described above is sufficiently exothermic that the
energy released can drive an endothermic reaction in which inorganic
phosphate from the cytoplasm can be added to our PGAL molecule to
form 1,3 biphosphoglyeric acid. The enzyme responsible is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenenase.
The reaction described above is sufficiently exothermic that the
energy released can drive an endothermic reaction in which inorganic
phosphate from the cytoplasm can be added to our PGAL molecule to
form 1,3 biphosphoglyeric acid. The enzyme responsible is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenenase.
|
|
|